electron affinity of sodium|electron affinity vs electronegativity : Cebu Electron affinity can be defined in two equivalent ways. First, as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom. The second (reverse) definition is that electron affinity is the energy required to remove an electron from a singly charged gaseous negative ion. The latter can be regarded as the ionization energy of the –1 ion or the zeroth ionization energy. Either convention can be used. Understanding the difference between had and have is key to mastering English grammar.Have is used to show possession or to indicate that an action relates to the present or future. For example, “I have a book” means you own a book now. On the other hand, had is the past tense of have, meaning it shows possession or an action .
PH0 · trend for electron affinity
PH1 · electron affinity vs electronegativity
PH2 · electron affinity trend and exceptions
PH3 · electron affinity chart
PH4 · determining electron affinity
PH5 · Iba pa
They have some of the best slot machines to play in Vegas in 2022; Luxor Las Vegas — In Luxor, slot denominations start from $0.01 up to $100. This is definitely a place to look for the loosest slots in Vegas since the casino still owns some traditional “reel” machines.
electron affinity of sodium*******Ago 11, 2023 Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative .Electron affinity can be defined in two equivalent ways. First, as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom. The second (reverse) definition is that electron affinity is the energy required to remove an electron from a singly charged gaseous negative ion. The latter can be regarded as the ionization energy of the –1 ion or the zeroth ionization energy. Either convention can be used. Electron affinity of Sodium is 52.8 kJ/mol. In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as: the change in energy (in .Use the trends in electron affinities going down a column for elements in the same group. Similarly, use the trends in electron affinities from left to right for elements in the same .The electron affinity of an element is the energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. A fluorine atom in the gas phase, for example, gives off energy .electron affinity vs electronegativityA representation of the atomic spectrum of sodium. Ionisation Energies and electron affinity. The electron affinity of sodium is 52.8 kJ mol ‑1. The ionisation energies of sodium are given below. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative .The electron affinity ( Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state .Glossary. GroupA vertical column in the periodic table. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. PeriodA horizontal row . Definition of Electron Affinity. Electron affinity is a quantitative measurement of the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher the electron affinity and the more easily an electron is added to an atom. Electron affinity can be .The first electron affinity is the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous atoms each acquire an electron to form 1 mole of gaseous -1 ions. It is the energy released (per mole of X) when this change happens. First electron affinities have negative values. For example, the first electron affinity of chlorine is -349 kJ mol-1. By convention, the .The electronic affinity is amount of energy, that is released during the attachment of the electron to the neutral atom. As a result of such attachment, a negative ion (anion) is formed. . This is the case, for example, in the case of sodium-chlorine (Na-Cl) bonding in sodium chloride. Electronic affinity is measured (or calculated .A wave function of the form Φ = ϕ (r 1, r 2) (1 + c r 12) is assumed for the (3 s) electrons of Na −, to take into account the polarization effect of the added electron, an effect neglected by the Hartree method. On this basis the electron affinity of sodium is calculated to be +1.2 ev and therefore the negative ion is stable. Chemical bonding - Electron Affinity, Intermolecular Forces, Covalent Bonds: Third in importance for bond formation after size and ionization energy is the energy change accompanying the attachment of electrons to a neutral atom. . The ionization energy of sodium is larger than the electron affinity of chlorine, so energy is required . Sodium (Na):-53 kJ mol . Electron affinity is almost zero or low in elements having a stable electronic configuration. This is due to the small tendency to accept another electron. Electron affinities of inert gases are zero. This is due to their atoms having stable ns²np⁶ configuration in their shell. Electron affinity of Beryllium, and .A7: Electron Affinities. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion. X(g) +e− → X−(g) + energy (A7.1) (A7.1) X ( g) + e − → X ( g) − + e n e r g y.Electron Affinity. The electron affinity (EA) of an element E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: [latex]E_{(g)}+e^- \rightarrow E^-_{(g)} \;\;\; \text{energy change=}EA \label{7.5.1}[/latex] Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is required to .Electron Affinity. Electron affinity is defined as the change (gain or loss) in energy (kJ mol−1) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion. . Thus, naphthalene-sodium in THF solution initiates easy and complete polymerization of α-methylstyrene whose electron . Electron Affinities. Electron affinity, often abbreviated as EA, is the energy released when an electron is added to a valence shell of the atom. F (g) + e- -> F-(g) EA = -328 kJ/mol. [When an electron is added to an . Chlorine - Electron Affinity. In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as: the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion. . Sodium is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in .electron affinity of sodium electron affinity vs electronegativity22. Organic Chemistry 5h 6m. 23. Chemistry of the Nonmetals 2h 39m. 24. Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds 3h 14m. The electron affinity of sodium is lower than that of lithium, while the electron affinity of chlorine is higher than that of fluorine. Suggest an explanation for this observation. The electronic properties (the HOMO and LUMO energy levels as well as the electron affinity) of the active positive electrode materials were also computed to rationalize the predicted redox potentials. 2.1.3. Correlation of electron affinity – solvation energy – redox potential First Ionization Energy of Sodium is 5.1391 eV. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom. X + energy → X+ + e−. where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X + is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and e − is the .
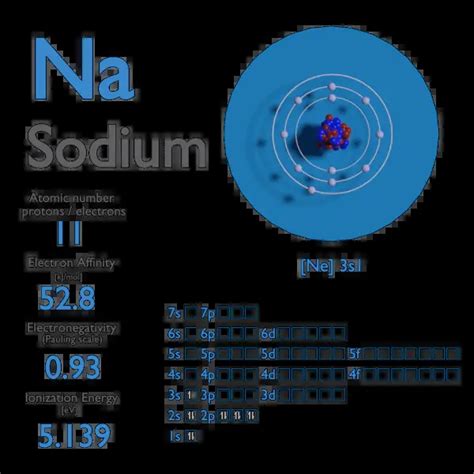
Hi there. Let's talk about electron affinity. Electron affinity is a measure of the likelihood of an atom to gain an electron. Thes are negative because they show the amount of energy released, so they're negative amounts of energy. So a greater negative number means a greater amount of energy released and a greater electron affinity. Calcium has two electrons in its outermost shell. So it will tend to lose those electrons not to gain one extra electron. This means electron affinity of calcium is less than that of fluorine. So fluorine is definitely not the answer (as we have to find an element with the least electron affinity). Sodium and potassium both have one electron in .The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity for an added electron) are those with the smallest size and highest ionization energies and are located in the upper right . Electron Affinity of Sodium is 52.8 kJ/mol. Electronegativity of Sodium is 0.93. Electron Affinity. In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as: the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
Explore Exclusive Credit Card Benefits, Rewards and Offers Available to Amex Card Members. Find Benefits that Work for Your Lifestyle. Learn More Today!
electron affinity of sodium|electron affinity vs electronegativity